Methodology
Game Design
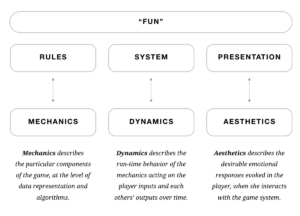
MDA: A Formal Approach to Game Design and Game Research
This seminal game design paper by Robin Hunicke, Marc LeBlanc, Robert Zubek lays out MDA as a formal approach to understanding games.
- Mechanics (the particular components and rules of a game)
- Dynamics (what happens when the Mechanics of a game are interacted with by players)
- Aesthetics (the emotional responses evoked by a player when they encounter the Dynamics)
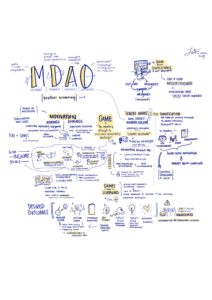
MDAO:
This book chapter by Heather Browning expands the MDA Model for use in creating games for effective clinical interventions. But it is quite useful anywhere that we need to design and create something for a particular outcome.
- Mechanics (the particular components and rules of a game)
- Dynamics (what happens when the Mechanics of a game are interacted with by players)
- Aesthetics (the emotional responses evoked by a player when they encounter the Dynamics)
- Outcomes (the desired consequence brought about by a player when they feel the Aesthetics)
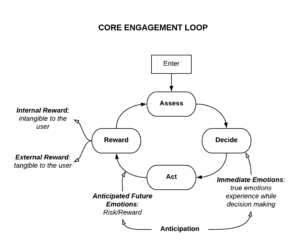
Core Engagement Loop:
Assess: What are our choices?
Decide: What do you really desire?
Act: Make the decision
Reward: The compelling experience
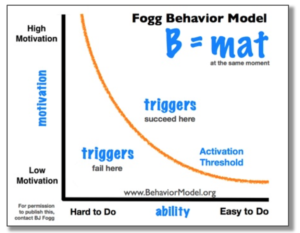
Behavior Design
- Motivation
- Ability
- Trigger
Creating Persuasive Technologies: An Eight-Step Design Process (Dr. BJ Fogg)
- Choose a simple behavior to target
- Choose a receptive audience
- Find what prevents the target behavior
- Choose a familiar technology channel
- Find relevant examples of persuasive technology
- Imitate successful examples
- Test and iterate quickly
- Expand on success
Neuroscience
Chemicals that affect our brains
- Dopamine: known as the feel-good neurotransmitter—a chemical that ferries information between neurons. The brain releases it when we do things that we crave, contributing to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction as part of the reward system.
- Epinephrine: a natural hormone also known as adrenaline. Strong emotions such as fear or anger cause epinephrine to be released into the bloodstream, which causes an increase in heart rate, muscle strength, blood pressure, and sugar metabolism.
- Norepinephrine: stress hormone and neurotransmitter that is released into the blood as a stress hormone when the brain perceives that a stressful event has occurred
- Oxytocin: the “hug drug” is a hormone and a neurotransmitter that is involved in childbirth and breast-feeding. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth.
- Serotonin: the key hormone and neurotransmitter that stabilizes our mood, feelings of well-being, and happiness. It also modulates cognition, reward, learning, and memory.
Emotional Design (Falcao, Soares, et al.)
- Visceral Design
- Behavior Design
- Reflective Design