The Four Phases of Games and Interest
Imagine a world where you can learn anything you want, anytime you want, and anywhere you want. A world where you can master a new language, explore a new culture, or discover a new passion with just a few clicks. A world where you can have fun, be creative, and challenge yourself while expanding your horizons. Sounds too good to be true, right? Well, not anymore.
Thanks to the power of digital learning experiences, this world is now within your reach.
In this article, we will show you how digital learning experiences can transform your education and your life, using the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development as a framework.
We will also give you some examples of video games and gamified learning experiences that use this model to drive towards intrinsic motivation. By the end of this article, you will be inspired to embark on your own digital learning journey and unleash your full potential.
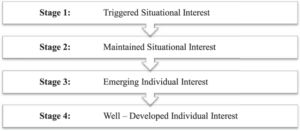
The Four-Phase Model of Interest Development is a theoretical framework that describes how a person’s interest in a topic or activity can evolve over time. It was proposed by researchers Suzanne Hidi and K. Ann Renninger in 2006. According to this model, there are four phases of interest development:
- Triggered situational interest: This stage arises when something in your environment captures your attention or sparks your curiosity, often something novel, unexpected, or challenging. It is typically short-lived and depends on external stimuli that trigger it.
- Maintained situational interest: This phase occurs when your interest and engagement in a subject or activity are driven by the elements that facilitate your learning, such as the content, the instructor, your peers, or the feedback received. This stage can endure longer than the initial interest and has the potential to deepen your learning and comprehension.
- Emerging individual interest: This phase happens when your affinity for a subject or activity intensifies due to your existing knowledge, personal desires, values, and self-concept. It endures for a more extended period and possesses greater strength compared to situational interest, motivating you to pursue further learning and engagement.
- Well-developed individual interest: This stage occurs when you possess an enduring passion that imbues you with a strong sense of knowledge and proficiency in a particular subject or activity. It compels you to invest significant time and effort willingly. This phase represents the utmost level of self-motivated and independent interest, capable of profoundly influencing your identity and pursuits.
The model considers both affective and cognitive factors that are involved in the development and deepening of interest. It also suggests that educators can play an important role in facilitating interest development by providing appropriate triggers, supports, challenges, and feedback for learners at different phases of interest.
One popular video game that takes the player through all four phases of the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development is Journey, an award-winning game about exploring a mysterious and beautiful desert world. Here is how the game achieves each phase differently:
Triggered situational interest: The game starts with a striking image of a lone figure in a vast desert, with a shining mountain in the distance. The player is immediately intrigued by the setting and the goal, and wants to find out more about the world and the story. The game also uses dynamic music and sound effects to create a captivating atmosphere and mood.
Maintained situational interest: The game keeps the player engaged by introducing new environments, challenges, and secrets along the way. The game also provides feedback and rewards for the player’s actions, such as unlocking new abilities, finding hidden symbols, and discovering ancient ruins. The game also supports the player’s interest by allowing them to interact with other players online, who can help or hinder them in their journey.
Emerging individual interest: The game develops the player’s personal preference and liking for the game by appealing to their emotions, values, and self-concept. The game creates a sense of wonder, awe, and beauty through its stunning visuals and music. The game also evokes a range of emotions, such as joy, sadness, fear, and hope, through its narrative and gameplay. The game also reflects the player’s identity and personality through their choices, actions, and interactions with other players.
Well-developed individual interest: The game nurtures a strong emotional connection and a high level of knowledge and skill for the game by challenging and rewarding the player in different ways. The game offers multiple endings and secrets that depend on the player’s performance and decisions. The game also encourages the player to replay the game and explore different paths and possibilities. The game also fosters a sense of community and belonging among the players who share their experiences and stories online.
Gamified learning experiences can also use the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development to drive towards intrinsic motivation by designing their content, activities, and feedback in ways that can trigger, maintain, foster, and nurture the learner’s interest in the topic.
One example of a successful gamified learning experiences that uses the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development to drive towards intrinsic motivation is Duolingo, a language learning app. It uses gamification elements such as points, levels, badges, streaks, leaderboards, and rewards to motivate learners to practice their language skills. But it also uses narrative and immersion techniques to foster a deeper connection with the learner, especially with their recent AI-driven features.
Triggered situational interest: Duolingo triggers situational interest by presenting a variety of topics, exercises, and stories that are relevant, novel, and challenging for the learners. For example, learners can choose from over 40 languages to learn, from Spanish and French to even Klingon. Learners can also select from different courses that match their goals, such as travel, culture, or career. Learners can also access interactive stories that immerse them in different scenarios and contexts. Duolingo also uses dynamic music and sound effects to create a captivating atmosphere and mood.
Maintained situational interest: Duolingo maintains situational interest by providing feedback, guidance, and reinforcement for the learners’ progress and performance. For example, learners can earn points, level up, unlock new skills, and collect badges as they complete their lessons. Learners can also see their progress and improvement through the app’s dashboard, which shows their fluency score, streak count, and XP rank. Learners can also receive tips, explanations, and corrections from the app’s AI tutor, which helps them learn from their mistakes and master the language concepts. Duolingo also supports the learners’ interest by allowing them to interact with other learners online, who can help or hinder them in their journey. For example, learners can join clubs, compete in leagues, chat with friends, and send each other virtual gifts.
Emerging individual interest: Duolingo fosters emerging individual interest by allowing learners to customize their goals, preferences, and learning paths, as well as reflect their values and identity through the language they choose to learn. For example, learners can set their daily goals, choose their preferred learning style, and adjust their difficulty level. Learners can also follow their own pace and sequence of learning, and revisit the skills and topics they want to review or practice. Learners can also express their creativity and identity through the language they learn, as they can explore different cultures, histories, and perspectives through the app’s content and stories.
Well-developed individual interest: Duolingo nurtures well-developed individual interest by creating a sense of mastery, achievement, and enjoyment for the learners, as well as opportunities for socializing and sharing with other learners. For example, learners can access advanced features and exercises, such as podcasts, documentaries, and quizzes, that challenge and enrich their language skills. Learners can also earn certificates, trophies, and medals that recognize their accomplishments and proficiency. Learners can also have fun, be creative, and challenge themselves while expanding their horizons. For example, learners can access two new AI-powered features called Explain My Answer and Roleplay that are exclusive to Duolingo Max, a recent subscription tier that uses GPT-4 technology.
When developing a digital learning experience, incorporating the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development can help you create a motivating and engaging educational platform. Here are guidelines with specific examples for each phase:
Triggered Situational Interest:
Capture Attention: Start by presenting a captivating scenario, question, or challenge that piques learners’ curiosity. For example, if you’re developing a science learning app, begin with a thought-provoking question like, “What if you could explore the depths of the ocean without getting wet?”
Use Visuals and Multimedia: Employ engaging visuals, videos, or interactive elements to make the learning experience visually appealing and immersive. For instance, you could include 3D animations to explain complex concepts or a virtual tour for historical lessons.
Storytelling: Craft a narrative that draws learners in. Develop a story or scenario that relates to the subject matter. For a history lesson, create a time-travel adventure where learners can “visit” historical events and interact with key figures.
Challenge and Mystery: Introduce challenges or mysteries that require learners to explore and discover. For a math learning app, you could present a series of math puzzles with hidden clues and rewards for solving them.
Maintained Situational Interest:
Feedback and Progression: Provide immediate feedback on learners’ performance and progress. Use a point system, progress bars, or levels to show how they’re advancing. For example, in a language learning app, learners can earn points for each correct answer and see their progress on a fluency scale.
Variety and Exploration: Keep learners engaged by offering a variety of content formats, such as text, videos, quizzes, and interactive simulations. Allow them to explore different topics within the subject. For a geography app, include map quizzes, country profiles, and interactive geography games.
Social Interaction: Incorporate social features that allow learners to connect with peers, share achievements, and collaborate. In a coding platform, learners can join coding challenges, compete on leaderboards, and share their code for feedback.
Emerging Individual Interest:
Personalization: Let learners customize their learning experience. Allow them to set goals, choose the order of topics, and adjust the difficulty level. In a music theory app, learners can select their preferred instrument and genre to tailor the content to their interests.
Relevance to Real Life: Show learners how the subject matter relates to their daily lives or future goals. In a financial literacy course, provide practical examples of budgeting, saving, and investing that align with real-world scenarios.
Identity and Values: Create opportunities for learners to express their identity and values through the learning experience. In an art history app, allow learners to curate their virtual art gallery by selecting and interpreting artworks based on their personal perspectives.
Well-developed Individual Interest:
Mastery and Challenges: Offer advanced levels, challenges, or projects that require learners to apply their knowledge and skills in creative ways. In a coding platform, introduce complex coding projects where learners can build their own applications.
Recognition and Achievement: Recognize and celebrate learners’ achievements with certificates, badges, or trophies. In a photography course, award certificates for completing different modules and badges for achieving specific photography milestones.
Community and Sharing: Foster a sense of community by encouraging learners to share their experiences, insights, and projects. Create discussion forums or peer review systems where learners can engage with one another. For a cooking app, learners can share their recipes and cooking experiences in a community forum.
By implementing these guidelines and examples based on the Four-Phase Model of Interest Development and what has been successful in video games and gamified learning experiences, you can design a digital learning experience that not only motivates and engages learners but also fosters their intrinsic motivation and passion for the subject matter.
Read more on How Games Can Boost Your Learning.